A Comprehensive Introduction to Creating CSV Files in Python
Written on
Understanding CSV Files
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are a popular format for storing data due to their simplicity and compatibility with applications like Excel and Google Sheets. In this guide, we'll explore how to create and manipulate CSV files in Python without using the Pandas library. This approach can be particularly valuable for those who are new to Pandas or want to grasp the fundamentals of data formatting.

The structure of a CSV file is straightforward. Each entry in a data table is separated by commas, which define columns, while each line corresponds to a new row.
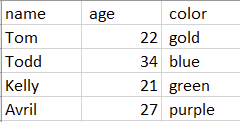
Let’s illustrate this with a simple example. If you create a text file in Notepad with the following content:
name, age, color Tom, 22, gold Todd, 34, blue Kelly, 21, green Avril, 27, purple
Saving this as a .csv file and opening it in Excel will display the data neatly in a tabular format.
Creating CSV Files in Python
Python provides several built-in methods to handle CSV files, including the csv module. However, for this tutorial, we will focus on constructing a CSV file manually to enhance our understanding of how CSVs function.
To replicate the previous example programmatically, we can break it down into manageable steps:
- Each column in the CSV is separated by a comma.
- Each row is delineated by a newline character.
- We will write these strings into a file using Python's built-in functions.
Let's construct the same table with Python code. We'll start by defining our data as comma-separated strings and store them in a list:
header = 'name, age, color' row0 = 'Tom, 22, gold' row1 = 'Todd, 34, blue' row2 = 'Kelly, 21, green' row3 = 'Avril, 27, purple' data_list = [header, row0, row1, row2, row3]
Next, we open a new file in write mode, which allows us to input our data:
my_file = open('data.csv', 'w')
Now, we can write our entries into the file one at a time:
for row in data_list:
my_file.write(row)
my_file.write('n')
Finally, we close the file to save our work:
my_file.close()
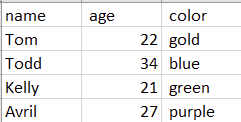
Now, when you open this file in Excel, it will display the same table as before.
Exploring Additional Resources
To further enhance your understanding of handling CSV files in Python, check out the following videos:
The first video, Python Tutorial: CSV Module - How to Read, Parse, and Write CSV Files, provides an overview of how to effectively use the CSV module in Python.
The second video, Python for Beginners: Reading & Manipulating CSV Files, dives into reading and processing CSV files, perfect for those starting out.
Final Thoughts
By now, you should have a clear understanding of the internal workings of CSV files and how to create them manually in Python. This foundational knowledge will assist you in effectively formatting and processing your data.
Until next time, happy coding! For more resources and guides, consider signing up for our weekly newsletter and joining our community.