The Similarities Between Other Stars and Our Sun
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Stellar Similarity
When gazing at the night sky, we notice a multitude of twinkling points. Some shine brightly while others are barely visible. Scientists have established that these celestial bodies are primarily composed of gas, mainly hydrogen and helium. But how did we arrive at this conclusion? Could there be alternative explanations for the stars we see from Earth? This intriguing question was raised by one of our subscribers from Ukraine. Let’s delve into it together.

The Historical Perspective on Stars
In the late 16th century, Giordano Bruno proposed that stars are akin to our Sun. However, for many years, astronomers lacked the technology to confirm this idea. By the latter half of the 17th century, most astronomers had embraced concepts similar to Bruno's, awaiting experimental validation.

The first experimental confirmations emerged in the early 19th century through the work of several astronomers, including V.Ya. Struve from Russia, F. Bessel from Germany, and T. Henderson from the United States. They measured the parallaxes of various stars, such as Vega, 61 Cygnus, and Alpha Centauri, determining their distances. This evidence highlighted that these stars had brightness levels comparable to the Sun.

Spectroscopy and Stellar Composition
German scientists G. Kirchhoff and R. Bunsen discovered that each chemical element produces a unique spectrum when interacting with radiation. This breakthrough allowed us to analyze the chemical composition of celestial bodies through spectral analysis.
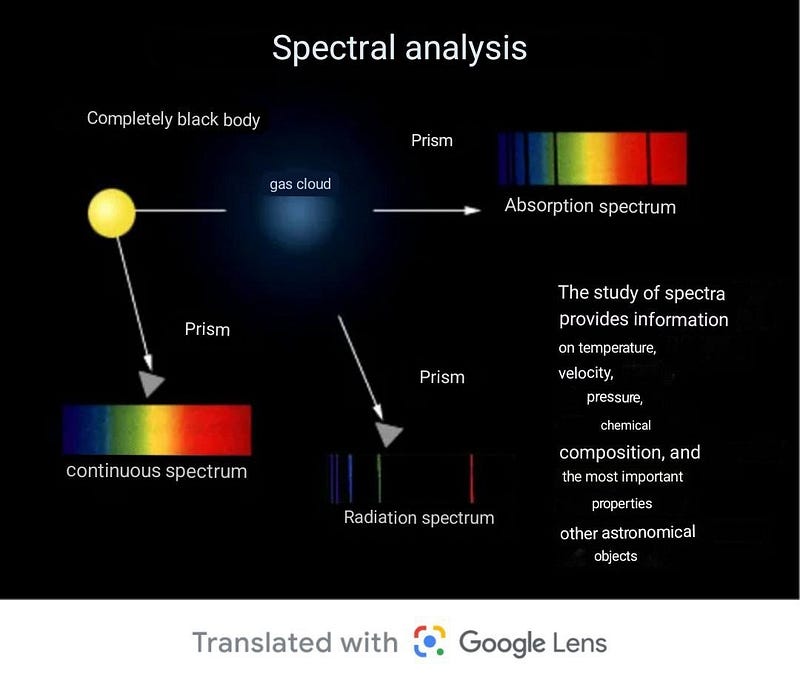
Through this method, we established that stars are predominantly made up of hydrogen and helium, the universe's most prevalent elements. Similarly, we found that the Sun is largely composed of these elements. In the early 20th century, astrophysicist Arthur Eddington elucidated how the Sun produces light through thermonuclear reactions that convert hydrogen into helium.
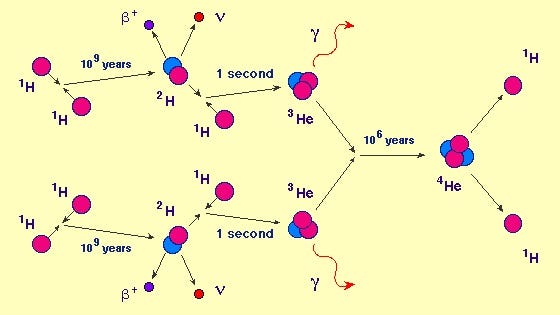
Understanding Thermonuclear Fusion
The conditions necessary for thermonuclear fusion, such as extreme temperatures and pressures, are typically found in massive celestial bodies. These conditions can arise from the gravitational compression of substantial amounts of matter.
Thanks to these scientific advancements, we comprehend that the stars we observe are located vast distances away but share luminosity comparable to our Sun. Furthermore, we recognize that their chemical compositions are strikingly similar, and we understand the conditions required for hydrogen and helium to emit light at such intensities.

Conclusion: Stars Like Our Sun
This accumulation of knowledge leads us to conclude that stars, much like the Sun, are immense gas spheres maintained by their own gravitational forces, generating energy through internal thermonuclear reactions. All observational data supports this understanding, including studies of star movements in binary and multiple systems, the formation of new stars and supernovae, the detection of heavier elements in star spectra, and the measurement of stellar surface temperatures.
Thus, the tiny points of light scattered across the night sky are indeed stars resembling our Sun, as their characteristics and properties align with those of our Sun, established over centuries of research.
Clap if you want to see more articles about space in your feed!
Subscribe to our channel and feel free to ask questions, which I will address in future articles.
If you appreciate my work, consider supporting me by joining Medium for just $5 a month, helping us create even better content.